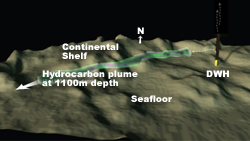
August 19, 2010, 2 p.m.Source: Media RelationsScientists at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) detected and characterized a plume of hydrocarbons that is at least 22 miles long and more than 3,000 feet below the surface of the Gulf of Mexico, a residue of the BP Deepwater Horizon oil spill. The work presents a forensic snapshot of the plume characteristics in June and is reported in a study appearing in the Aug. 19 issue of the journal Science. The researchers measured distinguishing petroleum hydrocarbons in the plume and, using them as an investigative tool, determined that the source of the plume could not have been natural oil seeps but had to have come from the blown out well. Moreover, they reported that deep-sea microbes were degrading the plume relatively slowly, and that it was possible that the 1.2-mile-wide, 650-foot-high plume had and will persist for some time. The WHOI team based its findings on some 57,000 discrete chemical analyses measured in real time during a June 19-28 scientific cruise aboard the R/V Endeavor, which is owned by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and operated by the University of Rhode Island. They accomplished their feat using two highly advanced technologies: the autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) Sentry and a type of underwater mass spectrometer known as TETHYS (Tethered Yearlong Spectrometer). “We’ve shown conclusively not only that a plume exists, but also defined its origin and near-field structure,” said Richard Camilli of WHOI’s Applied Ocean Physics and Engineering Department, chief scientist of the cruise and lead author of the paper. “Until now, these have been treated as a theoretical matter in the literature. “In June, we observed the plume migrating slowly [at about 0.17 miles per hour] southwest of the source of the blowout,” said Camilli. The researchers began tracking it about three miles from the well head and out to about 22 miles (35 kilometers) until the approach of Hurricane Alex forced them away from the study area. The study—which was enabled by three NSF RAPID grants to WHOI scientists with additional funding from the U.S. Coast Guard—confirms that a continuous plume exists “at petroleum hydrocarbon levels that are noteworthy and detectable,” said Christopher Reddy, a WHOI marine geochemist and oil spill expert and one of the authors of the study. The levels and distributions of the petroleum hydrocarbons show that “the plume is not caused by natural [oil] seeps” in the Gulf of Mexico, Camilli added. WHOI President and Director Susan K. Avery praised the WHOI scientists for their “prudence and thoroughness, as they conducted an important, elegant study under difficult conditions in a timely manner.”
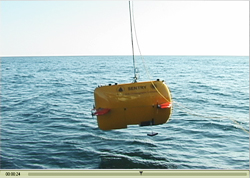
Persistent plume The plume has shown that the oil already “is persisting for longer periods than we would have expected,” Camilli said. “Many people speculated that subsurface oil droplets were being easily biodegraded. “Well, we didn’t find that. We found it was still there.” Whether the plume’s existence poses a significant threat to the Gulf is not yet clear, the researchers say. “We don’t know how toxic it is,” said Reddy, “and we don’t know how it formed, or why. But knowing the size, shape, depth, and heading of this plume will be vital for answering many of these questions.” The key to the discovery and mapping of the plume was the use of the mass spectrometer TETHYS integrated into the Sentry AUV. Camilli developed the mass spectrometer in close industrial partnership with Monitor Instruments Co. in Cheswick, Pa., through a grant from the National Ocean Partnership Program. The TETHYS--which is small enough to fit within a shoebox--is capable of identifying minute quantities of petroleum and other chemical compounds in seawater instantly. Sentry, funded by NSF and developed and operated by WHOI, is capable of exploring the ocean down to 14,764 feet (4,500 meters) depth. Equipped with its advanced analytical systems, it was able to crisscross plume boundaries continuously 19 times to help determine the trapped plume’s size, shape, and composition. This knowledge of the plume structure guided the team in collecting physical samples for further laboratory analyses using a traditional oceanographic tool, a cable-lowered water sampling system that measures conductivity, temperature, and depth (CTD). This CTD, however, was instrumented with a TETHYS. In each case, the mass spectrometers were used to positively identify areas containing petroleum hydrocarbons. “We achieved our results because we had a unique combination of scientific and technological skills,” said Dana Yoerger, a co-principal investigator and WHOI senior scientist. Until now, scientists had suspected the existence of a plume, but attempts to detect and measure it had been inconclusive, primarily because of inadequate sampling techniques, according to the WHOI scientists. In previous research, Yoerger said, “investigators relied mostly on a conventional technique: vertical profiling. We used Sentry and TETHYS to scan large areas horizontally, which enabled us to target our vertical profiles more effectively. Our methods provide much better information about the size and shape of the plume.” The researchers detected a class of petroleum hydrocarbons at concentrations of more than 50 micrograms per liter. The water samples collected at these depths had no odor of oil and were clear. “The plume was not a river of Hershey’s Syrup,” said Reddy. “But that’s not to say it isn’t harmful to the environment.”
No Unusual Oxygen Signals The scientists benefited not only from new technology but older methods as well. Contrary to previous predictions by other scientists, they found no “dead zones,” regions of significant oxygen depletion within the plume where almost no fish or other marine animals could survive. They attributed the discrepancy to a problem with the more modern measuring devices that can give artificially low oxygen readings when coated by oil. The team on Endeavor used an established chemical test developed in the 1880s to check the concentration of dissolved oxygen in water samples, called a Winkler titration. Of the dozens of samples analyzed for oxygen only a few from the plume layer were below expected levels, and even these samples were only slightly depleted. WHOI geochemist Benjamin Van Mooy, also a principal investigator of the research team, said this finding could have significant implications. “If the oxygen data from the plume layer are telling us it isn’t being rapidly consumed by microbes near the well,” he said, “the hydrocarbons could persist for some time. So it is possible that oil could be transported considerable distances from the well before being degraded.”
A Rapid Response The NSF RAPID program, which provides grants for projects having a severe urgency and require quick-response research on natural disasters or other unanticipated events, significantly speeded up the acceptance of the WHOI proposals. “In contrast to the usual six-to-eighteen-month lead time for standard scientific proposals, our plume study was funded two days after the concept was proposed to NSF and went from notification of the proposal’s acceptance to boarding the Endeavor in two-and-a-half weeks,” Reddy said. Within days of being notified of the award, Reddy said the WHOI team reached out to NOAA, offering assistance in the laborious, but important, process of collecting and analyzing water samples for natural resource damage assessment (NRDA). In addition to conducting the work NSF funded, the WHOI team worked cooperatively with NOAA to collect data that will be used to determine damages and calculate a fair settlement for those affected by the massive spill. “Doing a NRDA cruise is not a trivial effort. It requires a tremendous amount of coordination -- from accommodating additional on-board observers to ensure a chain of custody to arranging for samples to be ferried from the research vessels every few days,” said Avery. “I’m very proud of what this team has accomplished. “Very good science was done that will make a big difference,” Avery added. “This cruise represents an excellent example of how non-federal research organizations can work with federal agencies and how federal agencies can work together to respond to national disasters.” "This research illustrates the value of NSF's long-term investment in state-of-the-art technology like Sentry so that it can be deployed not only to advance basic knowledge but also in national emergencies," said David Conover, director of NSF's Division of Ocean Sciences. “Similarly, the NSF RAPID award program enables scientists to quickly arrive on the scene and begin rigorous study of episodic events like this oil spill.” NSF has so far issued a total of 90 RAPID grant awards to investigators; the grants to date are worth $10.2 million for study of the spill. NSF has invested an additional $3 million in ship-related operating costs. "The payoff occurs when peer-reviewed results like these reported today are made public," said Conover. While at sea, these scientists, who are experienced in the study of oil spills and natural oil seeps, faced unusual challenges from the extreme heat, water rationing, exposure to crude oil and its vapors, and 24-hour-a-day operations enabled by the URI crew. Along with their own scientific objectives, the team also bore in mind the advice of top science officials speaking at a June 3 Gulf Oil Spill Scientific Symposium at Louisiana State University, who cautioned researchers about the importance of verification and proceeding in a scientific manner: “We are all served best by proceeding in a careful, thoughtful, and quantifiable manner, where we can actually document everything and share it publicly,” NOAA Administrator Jane Lubchenco told those assembled. At that meeting, US Geological Survey Director Marcia McNutt underscored the need for peer review of interpretive results before they are released, saying "There's nothing that throws the community into dead ends faster” than to have [poor] data out there. Assistant Director of NSF Tim Killeen also echoed the sentiment that “quality assurance and quality control are essential for thorough work.” “WHOI scientists attending this meeting took this advice to heart and used it as a guiding light for proper dissemination of scientific information,” Reddy said. Reddy said the results from this study and more samples yet to be analyzed eventually could refine recent estimates about the amount of the spilled oil that remains in the Gulf. Camilli said he and his WHOI colleagues are considering a new research proposal to look for more plumes. Reddy said the WHOI team members know the chemical makeup of some of the plume, but not all of it. Gas chromatographic analysis of plume samples confirm the existence of benzene, toluene, ethybenzene, and total xylenes—together, called BTEX at concentrations in excess of 50 micrograms per liter. “The plume is not pure oil,” Camilli said. “But there are oil compounds in there.” It may be “a few months of laboratory analysis and validation,” Reddy said, before they know the entire inventory of chemicals in the plume. Camilli attributed the project’s success to WHOI’s wide range of expertise and scientific capabilities. He contrasted that with “what the oil industry does best: They know where to drill holes and how to get the oil to come out. WHOI’s expertise in oil spill forensics, marine ecological assessment, and deep submergence technology development will be essential for our nation as it updates its energy policy and offshore oil production confronts the challenges of deepwater operations.” Other WHOI members of study team included Assistant Scientist James C. Kinsey and Research Associates Cameron P. McIntyre and Sean P. Sylva. The research team also included Michael V. Jakuba of the University of Sydney, Australia, and a graduate of the MIT/WHOI joint program in Oceanographic Engineering, and James V. Maloney of Monitor Instruments Co.
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution is a private, independent organization in Falmouth, Mass., dedicated to marine research, engineering, and higher education. Established in 1930 on a recommendation from the National Academy of Sciences, its primary mission is to understand the ocean and its interaction with the Earth as a whole, and to communicate a basic understanding of the ocean's role in the changing global environment.
Originally published: August 19, 2010 Last updated: May 1, 2011 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Copyright ©2007 Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, All Rights Reserved, Privacy Policy. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||